- Author Horace Young young@householdfranchise.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:35.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:41.
Epidural anesthesia is a method of pain relief at childbirth, due to which pain is blocked only in the lower part of the body, while the woman in labor feels contractions and remains conscious. Spinal anesthesia is given with an injection into the spine.
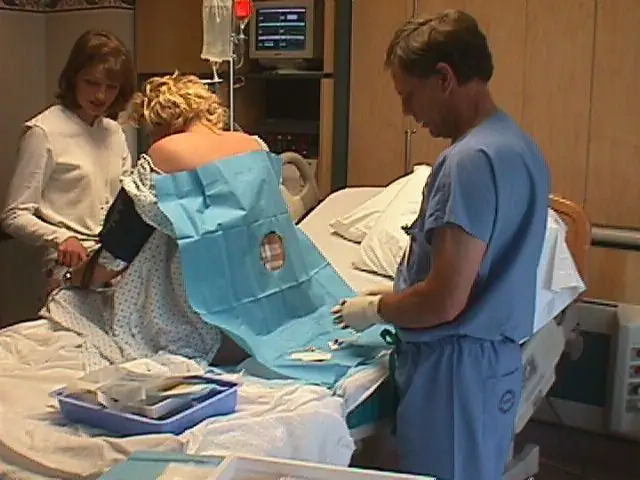
Epidural anesthesia during childbirth and its benefits
Spinal pain relief during childbirth does not affect the consciousness of the child's mother when pain is weakened or completely lost. The absence of the effect of epidural anesthesia on the fetus has been proven. Thanks to this method of pain relief, the process of childbirth is accelerated if the slowdown is caused by the mother's anxiety (it blocks the production of stress hormones - adrenaline and norepinephrine). Epidural anesthesia has a beneficial effect on women in labor with high blood pressure.
Epidural Anesthesia: Implications
The tasks of the anesthesiologist include the prevention of adverse reactions during the procedure of anesthesia. Although the risk of serious complications after epidural anesthesia is small, in some cases, side effects cannot be avoided.
Spinal anesthesia during childbirth can cause heaviness in the legs, feeling of numbness, trembling. After the expiration of the action of the drug, this reaction of the body disappears.
For pregnant women with low blood pressure, this type of pain relief can be dangerous due to its hypotonic effect, but the anesthesiologist can administer special medications that increase blood pressure.
Allergic reactions are possible, so it is important for a pregnant woman to warn the attending physician about which drugs she is allergic to.
In rare cases, epidural anesthesia may cause breathing problems due to the effect of drugs on the muscles of the chest, oxygen supply in this case is possible through a mask, and this side effect disappears simultaneously with the cessation of the pain relief.
If a drug used for spinal anesthesia gets into the venous bloodstream, it can disrupt the work of the heart and cause loss of consciousness. The risk of complications is low, since the anesthesiologist makes sure that the needle is not in the vein before administering the medication.
It happens that the use of epidural anesthesia during childbirth does not give the expected effect, then the dose of the drug can be increased, or another method of pain relief can be used.
It happens that during the installation of the catheter, the woman in labor feels a feeling of a lumbago in the back, but it passes very quickly and does not cause further inconvenience.
After giving birth with spinal anesthesia, back pain may persist at the site of the needle placement, but in most cases it will go away quickly.
Some women in labor report headaches after epidural anesthesia. They may be due to the fact that the catheter has penetrated during insertion beyond the epidural space. To reduce the risk of this complication, do not move during the puncture.
Spinal anesthesia also has side effects such as nerve damage, paralysis of the lower extremities, bleeding into the epidural space, but the risk of developing them is negligible.






